Exercises
ANSWER IN BRIEF
Q.1. Look at the diagram showing the positive feedback mechanism on page 13. Can you list the inputs that went into tool making ?What were the processes that were strengthened by tool making ?
Diagram on page-13
Answer:-
According to the diagram of the positive feedback mechanism, following are the inputs that went into tool making:-
- Upright walking
- Hands freed for using tools, carrying infants and objects
- Increase in brain size and capacity of brain
- Visual surveillance, long distance walking while foraging and hunting.
Following is the list of processes that were strengthened by tool making:-
- Upright walking
- Increase in brain size and capacity of brain
- Visual surveillance, long distance walking while foraging and hunting.
Q.2. Humans and mammals such as monkeys and apes have certain similarities in behaviour and anatomy. This indicates that humans possibly evolved from apes. List these resemblances in two columns under the headings of (a) behaviour and (b) anatomy. Are there any differences that you think are noteworthy?
Answer:-
There are some noteworthy differences between humans and apes in terms of behaviour and anatomy. Anatomically, Humans have larger size of brain-case than that of apes. Upper and lower jaws of apes is larger than that of humans. Apes have denser body hair than that of humans. In terms of behaviour, humans are much different than apes. Human have well developed language, which is lacking in apes. Humans are able to use upper limb in a much better way than apes. Humans can walk and run on two lower limbs in a much better way than apes.Q.3. Discuss the arguments advanced in favour of the regional continuity model of human origins. Do you think it provides a convincing explanation of the archaeological evidence ? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:-
According to the regional continuity model (with multiple regions of origin) of human origin, archaic homo sapiens evolved in different regions in different rates into modern humans. This is the reason why appearances of modern humans in different parts vary even if they share the same region. This model looks more convincing than replacement model with reference to the origin of humans because various archaeological sites have been discovered in different geographical regions. The appearances of modern humans vary geographically. For instance, people in South Africa are black in body color, while in Australia people are white in body color. Even if a person of South African origin moves to North America or Australia, his body color does not become white, but it is possible that there would be seen variations in his future generations gradually, making appearance of future generations different than their forefathers.
Archaeological evidences are given below -
Q.4. Which of the following do you think is best documented in the archaeological records: (a) gathering, (b) tool making, (c) the use of fire.
Answer:-
Tool making is the best documented in archaeological records because they were made of hard materials, i.e. stones and bones of animals, and hence they could have been remained for much longer time. Even if they were buried under mounds they were not destroyed. Earliest evidence for making and use of stone tools come from sites in Ethiopia and Kenya. The earliest stone tool makers were the Australopithecus. Tools were made by both women and men, but women made tools for obtaining food for themselves as well as to sustain their children after weaning. Men made tools for hunting and breaking land for cultivation.
Answer in short Essay
Q.5. Discuss the extent to which (a) hunting and (b) constructing shelters would have been facilitated by the use of language. What other modes of communication could have been used for these activities ?
Answer:-
Use of language proved milestone in arts such as hunting and constructing shelters in ancient time. Language may be prominently divided into two categories - (i) Sound, and (ii) sing. Sound language may again be divided into two parts - (i) verbal communication, and (ii) non-verbal communication. And sign language may be divided into two types - (i) hand gestures, (ii) symbols on hard surfaces such as stones, walls, caves etc.
Early humans like hominids may have communicated in either sign language like hand gestures and paintings on caves, or non-verbal communication such as singing or humming. This helped them gather in groups for numerous purposes, such as hunting, making shelters, etc. Cave-paintings in various sites depicted animals, birds, humans, etc. Humans have been depicted as hunting, fishing, fighting wars etc. This might have indicated that early people gathered in these caves to learn the techniques of hunting. As the early people lived in forests, they had to protect themselves from wild animals. This inspired they to make gather and live together in groups. When they used to be danger they produce non-verbal sounds like humming or singing to get in groups in order to fight the danger. Gradually they began to construct shelters for themselves for their safety from wild animals and harsh weathers.
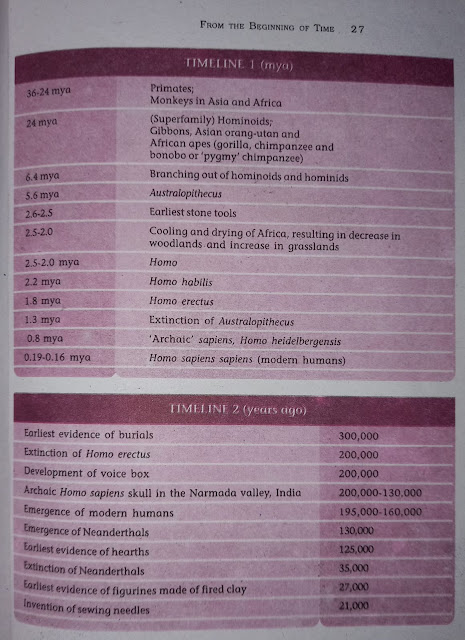
Table of Timeline-1 and Timeline-2
Q.6. Choose any two developments each from Timeline 1 and 2 at the end of the chapter and indicate why you think these are significant?
Answer:-
Table-1
2.2 mya - Homo habilis
This was a significant period in the process of human evolution. The significance of this period is evident from the following events:-
- Emergence of homo habilis class of early human. He was also known as 'skillful man'.
- He is attributed to discovery of stone tools.
- Remains of homo habilis has been found in eastern or southern Africa.
- Languages developed in this period alone.
1.8 mya - Homo erectus
This was a significant period in the process of human evolution. The significance of this period is evident from the following events:-
- Emergence of homo erectus, an 'upright man'.
- This class of early human learn to stand on two feet and freed his upper limb (hands) to use for other purpose such as carrying objects, infants and tools.
- This class of early human increased his visual power as he could see further distance by standing upright.
- Discovery of fire is attributed to none other than homo erectus.
- Tool making is also an important event that is attributed to homo erectus.
Table-2
Emergence of Neanderthals - 130,000 years ago
This period is significant in the process of human evolution because of the following reasons:-- The period witnessed the evolution of Neanderthals, a category of homo sapience class of early humans.
- They first appeared in Germany.
- He is called wise man.
- Our own species has evolved from homo sapience itself.
- Earliest evidence of hearths has been found at Terra Amata on the coast of southern France.
- These hearth were made inside the cave for various purposes, such as, cooking, warming up, scaring animals, lighting inside the cave, harden woods (tip of the spear), flaking of tools, etc.
- This shows that people in this time period had control over fire.



Comments
Post a Comment